Eating a Mediterranean diet can lower risk of depression, say researchers
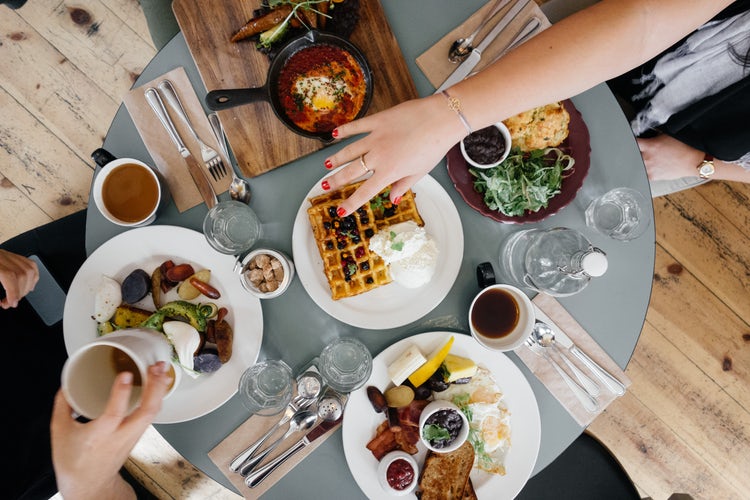

Eating a Mediterranean diet could significantly improve mental health, researchers at University College, London have found.
They said there was 'compelling' evidence that eating a diet with plenty of fish, vegetables, nuts and olive oil could lower the risk of developing depression by around a third.
The researchers believe the findings are significant enough that doctors and mental health practitioners should see 'dietary counselling' as a part of treating depression.
'There is compelling evidence to show that there is a relationship between the quality of your diet and your mental health,' Dr Camille Lassale said.
'This relationship goes beyond the effect of diet on your body size or other aspects of health that can in turn affect your mood.'
The researchers looked at 41 studies into the link between diet and depression, with four of the studies specifically analyzing the mental health benefits of a Mediterranean diet.
They found that strict followers of the Mediterranean diet were 33 per cent less likely to suffer from depression than those who did not follow the diet strictly.
Their findings, published in the latest edition of the Molecular Psychiatry journal, also found that people who ate higher quantities of saturated fat, sugar and processed food were at greater risk of depression.
Co-author Dr Tasnime Akbaraly said: 'Our study findings support routine dietary counselling as part of a doctor's office visit, especially with mental health practitioners.
'This is of importance at a patient's level, but also at public health level, especially in a context where poor diet is now recognised to be the leading cause of early death across middle and high-income countries and at the same time mental disorders as the leading cause of disability.'
The researchers also recommended that people stick to anti-inflammatory foods like fruits and vegetables, lentils, chickpeas, fish, olive oil and nuts.
'A pro-inflammatory diet can induce systemic inflammation, and this can directly increase the risk for depression,' said Dr Lassale.











